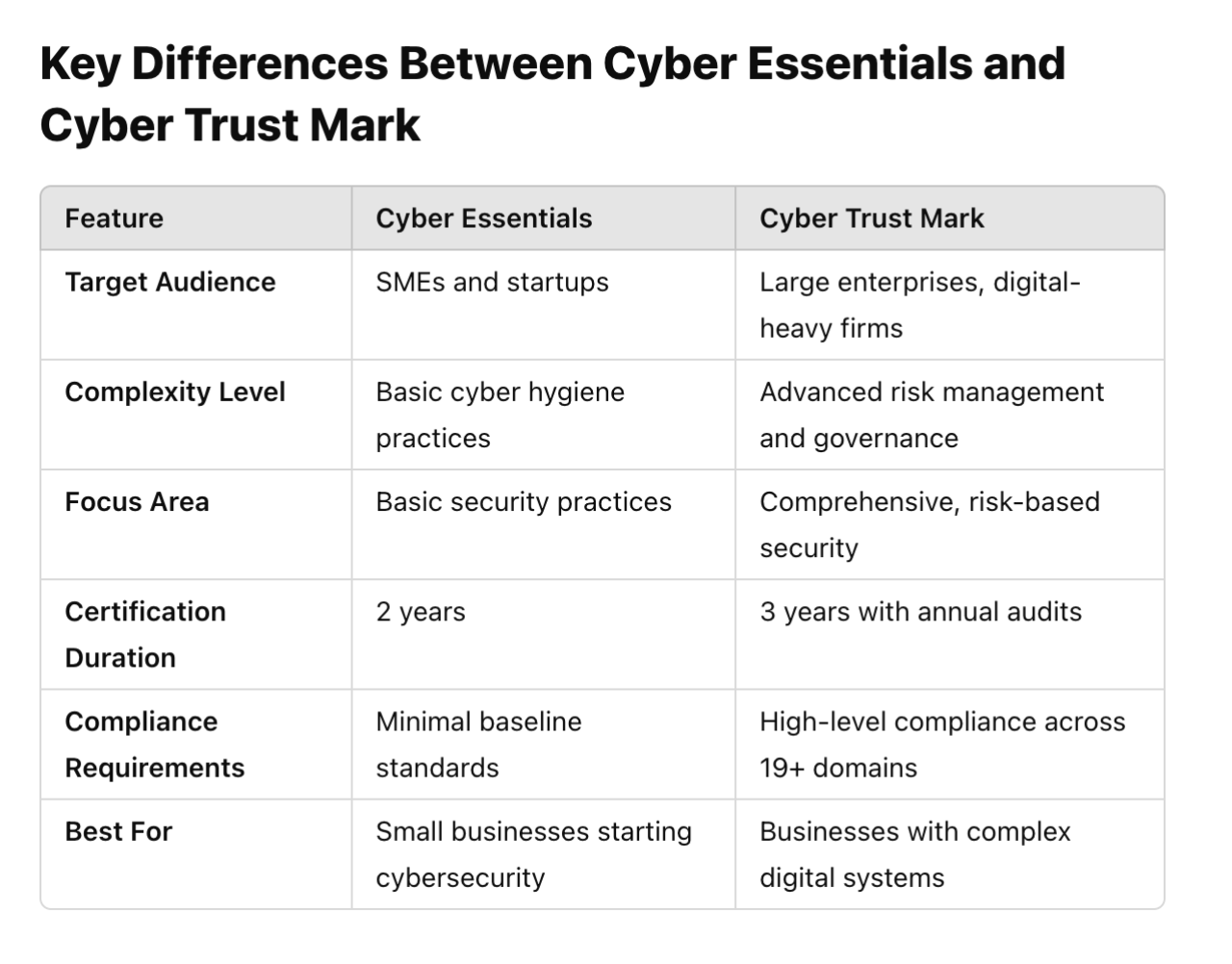
Cyber Essentials vs. Cyber Trust Mark: Key Differences for Singapore Businesses
The Cyber Essentials and Cyber Trust Mark certifications, developed by the Cyber Security Agency of Singapore (CSA), play a critical role in helping businesses strengthen their cybersecurity posture. However, understanding the differences between these two frameworks is essential for organizations looking to enhance data protection, meet compliance requirements, and build stakeholder trust.
This blog explores the distinctions between Cyber Essentials and Cyber Trust Mark, guiding Singapore businesses in choosing the right certification based on their size, risk profile, and cybersecurity maturity.
What is Cyber Essentials?
Cyber Essentials is a foundational cybersecurity certification for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in Singapore. It focuses on establishing basic cybersecurity hygiene to protect businesses from common cyber threats.
Key Features of Cyber Essentials:
✅ Asset Management: Maintain an inventory of software and hardware.
✅ Secure Configuration: Ensure systems are properly configured to minimize vulnerabilities.
✅ Malware Protection: Implement antivirus software and threat detection tools.
✅ Regular Software Updates: Ensure systems remain patched against the latest threats.
✅ Data Backup Management: Secure essential data through encrypted backups.
Who It's For: SMEs with limited IT resources start their cybersecurity journey.
Certification Validity: 2 years with the requirement for periodic reviews.
What is Cyber Trust Mark?
The Cyber Trust Mark is a more comprehensive certification designed for larger organizations with a higher risk profile and complex digital infrastructure. It takes a risk-based approach to cybersecurity, emphasizing advanced governance, risk management, and incident response capabilities.
Key Features of Cyber Trust Mark:
✅ Governance & Leadership: Requires defined cybersecurity leadership roles.
✅ Risk Management: Organizations must identify, assess, and mitigate cyber risks.
✅ Technical Security Controls: Advanced threat protection, encryption, and data segregation.
✅ Incident Response Plans: Formalized plans for managing cybersecurity incidents.
✅ Continuous Improvement: Regular security audits and employee training programs.
Who It's For: Larger or highly digitalized organizations with complex cybersecurity needs.
Certification Validity: 3 years with annual audits.
How to Choose the Right Certification for Your Business
✅ Choose Cyber Essentials If:
You’re an SME with limited cybersecurity infrastructure.
Your priority is to establish basic protections against common threats.
You’re looking for a cost-effective, entry-level certification.
✅ Choose Cyber Trust Mark If:
You’re a larger enterprise with complex cybersecurity needs.
Your business handles sensitive data requiring advanced security controls.
You need to meet higher compliance standards and regulatory expectations.
Benefits of Cyber Essentials and Cyber Trust Mark Certifications
🎯 1. Enhanced Data Protection
Both certifications promote better data protection standards, reducing the risk of data breaches.
🎯 2. Increased Customer Trust
Earning a cybersecurity certification signals to customers and partners that you take data security seriously.
🎯 3. Compliance with Singapore's PDPA
Both frameworks align with Singapore’s Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA), helping businesses comply with data privacy regulations.
🎯 4. Competitive Advantage
Certified businesses can stand out in tenders, partnerships, and collaborations that require high cybersecurity standards.
Steps to Get Certified in Singapore
Step 1: Understand Certification Requirements
Visit the CSA official website for the latest certification guides.
Familiarize yourself with the assessment criteria for both Cyber Essentials and Cyber Trust Mark.
Step 2: Conduct a Self-Assessment
Use CSA’s Cybersecurity Toolkit for SMEs to evaluate current cybersecurity measures.
Step 3: Engage a Certified Assessment Body (CAB)
CSA works with Certified Assessment Bodies (CABs) to assess businesses against certification requirements.
Examples of CABs in Singapore:
TÜV SÜD PSB
BSI Group Singapore
Step 4: Address Identified Gaps
Implement recommended security controls, such as firewalls, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and regular employee cybersecurity training.
Step 5: Submit for Certification
Complete the formal audit with a CAB and obtain the certification upon passing the assessment.
Conclusion: Which Certification Should Your Business Pursue?
Cyber Essentials and Cyber Trust Mark are vital in enhancing cybersecurity resilience for businesses in Singapore.
For SMEs: Start with Cyber Essentials to establish core cybersecurity defenses.
For Enterprises: Opt for the Cyber Trust Mark for comprehensive, risk-based protection.
By aligning with either of these certifications, businesses can strengthen their cybersecurity posture, protect sensitive data, and build trust with stakeholders in Singapore's evolving digital economy.